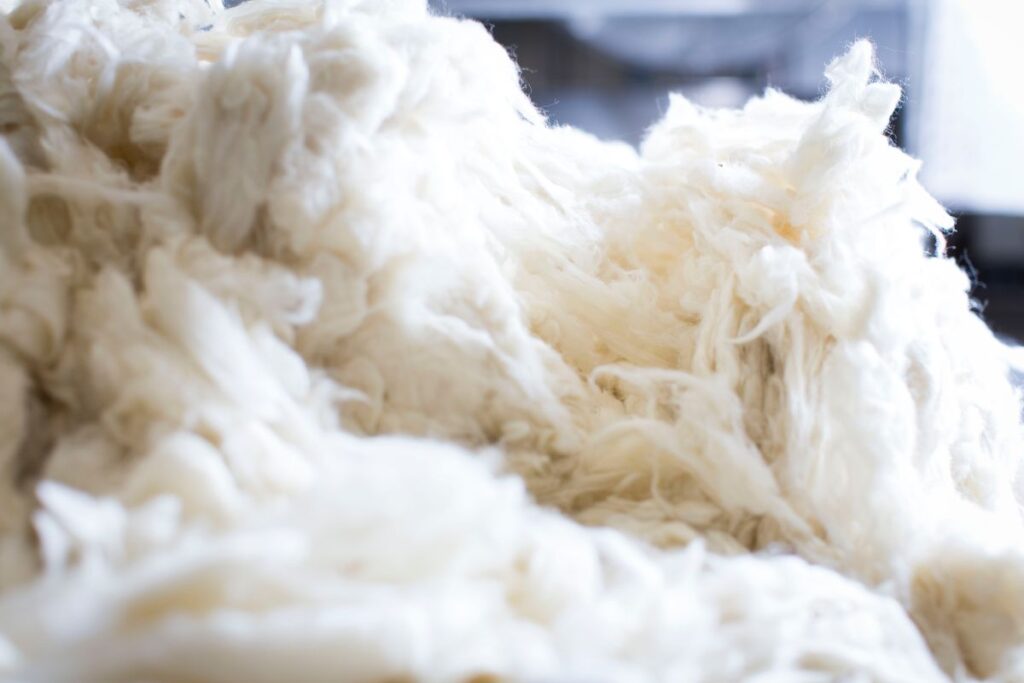
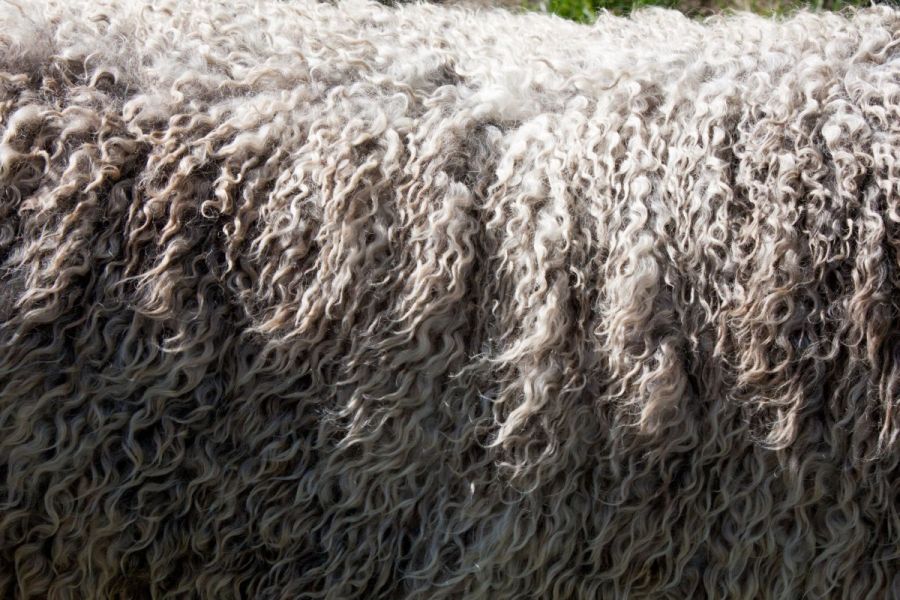
Wool is a general term for any fabric that is made from the fibre extracted from the fleece of a domesticated mammal. Differences between woollen and Worsted fabrics can be seen in the average fibre length of the yarn used to create them. Woolen fabrics are characterised by their tufted fuzzy appearance due to the use of short fibres in their weaving. They're cheap despite being bulkier and heavier than Worsted fabrics made from slightly longer yarns. When compared to other fabrics, worsteds stand out due to their hardness, smoothness, and subtle radiance. Wool can be knit or woven into a plain weave.
More categories, please Carpet wool, as its name suggests, is best suited for use in the creation of rugs. The fibres of this material are lengthy and coarse. "Apparel wool" refers to the high-quality wool that is woven into garments. Fabrics made from wool can be further categorised based on a number of different characteristics, including the animal used to create them, the weave used, the place in which the wool was bred, the fabric's texture, etc.
The Definition of Wool
Wool is a textile product constructed from animal hair, most commonly that of goats and sheep. Although sheep are the most common animal associated with the term "wool," farmers collect wool from a wide range of other species as well.
Pros of Using Wool
Durable Against Moisture
Wool's capacity to control moisture is a result of the synergy between its two fibre types. Due to its multi-layered construction, the outside is hydrophobic and impervious to rain and snow. The fibre is impermeable to liquid water, however it does allow water vapour to pass through. About 30 percent of wool's weight in water can be absorbed before it becomes noticeably damp to the touch.
Self-Cleaning Mechanism
As a result of the structure of its fibres, wool is capable of mechanical self-cleaning. The filament trunk's two types of fibres, which are intertwined like a liana, expand and contract to variable degrees when water is taken in and then released. By coming together so tightly, they set the wool fibre in motion. As the fibre moves, it dislodges any dust or grime that may have settled on its surface. These particles of filth don't penetrate the fibres, but rather sit on top. This characteristic of wool prevents it from easily picking up grime.
Self-Cleaning Substances
Wool's remarkable softness stems in part from its chemical self-cleaning capabilities. Due to their unique physical and chemical make-up, wool fibres are able to absorb and neutralise a wide variety of pollutants. Whether it's hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, dangerous polysaccharides based on benzene, or the components of cigarette smoke, wool "destroys" these foreign compounds. That's why wool clothes don't smell particularly bad when they're dirty.
Anti-static and Flame-Retardant
Finally, wool's ability to repel static electricity and burning is a nice benefit. Although wool can't be burned, synthetic textiles will melt at the slightest flame. Anyone who has felt a "spark" when touching a metal door handle or whose hair has stood on end after putting on clothing made of synthetic material can appreciate the benefits of wool's lack of static charge.
FAQs About Wool
The production of wool begins with the shearing of wool-bearing animals. Some animals bear wool once per year, and others bear wool multiple times throughout the year. Next, the shorn wool is cleaned and sorted into bales. There are a variety of ways to remove the greasy lanolin in raw wool, but most large wool producers use chemical catalysts for this process. Once the wool fibers are clean and sorted, they are carded, which is the process of making the fibers into long strands. These carded strands are then spun into yarn, and after a final washing, this yarn can be woven into garments and other types of woolen textiles.
Lastly, the finished textiles may be exposed to a variety of post-production processes to develop certain attributes. Fulling, for instance, is the immersion of a wool textile in water to make the fibers interlock, and crabbing is the process of permanently setting this interlock. Lastly, wool producers may decate their products for shrink-proofing purposes, and rarely, they may also dye their finished wool products.
Over the years, human beings have found hundreds of ways to use wool. While wool is primarily used in consumer applications, this substance is also popular in industrial applications for its durability and flame-retardant qualities. While finer types of wool might be used to make garments that directly contact the skin, it’s much more common to find wool used for outerwear or other types of garments that don’t make direct bodily contact. For instance, most of the world’s formal suits consist of wool fibers, and this textile is also commonly used to make sweaters, hats, gloves, and other types of accessories and apparel.
According to World Atlas, Australia produces 25 percent of the world’s wool, which makes it the most prominent wool-producing country. China, which has one of the world’s largest textile markets and textile industries, produces 18 percent of the world’s wool. At 17 percent, the United States is the third-largest wool producer, and New Zealand comes in fourth since it produces 11 percent of the world’s wool supply.
Wool and Its Many Varieties
Merino Wool
Merino wool is highly sought after and widely used. Most of the merino sheep in the world are raised in Australia, and its wool is used in a wide range of goods. This wool has a diameter of just 20 microns, making it another option among the finest on the market. Despite Spain's status as the country where the merino sheep was first domesticated, very little merino wool is currently being produced in the country. As a result of its greasy natural state, lanolin must be removed from merino wool before it can be spun into yarn.
Cashmere Wool
Cashmere, an exceptionally luxurious and luxuriously soft variety of wool, is also extremely expensive. Kashmir, in northern India, is home to the cashmere goats whose wool is used to create cashmere goods. Hair lengths in cashmere can be as short as 18 microns, making it just as delicate and soft as merino wool. The high price of cashmere wool is a result of its scarcity and great demand; cashmere goats only generate roughly 150 grammes of wool per year.
Border Leicester Wool
Beautiful Border Leicester wool fabric is named after the area of England that has long been home to the Border Leicester long wool breed sheep. This durable material will last for years and years. It's commonly used to create outerwear and clothing.
Cheviot
To make the coarse wool used to make Cheviot cloth, sheep are bred in the Cheviot hills of England, thus the name. The word is now commonly applied to woollen fabrics of medium to heavy weight that have a similar shaggy surface texture. Coatings made from the fabric are very popular.
Shetland Wool
This fabric uses wool from Scottish sheep. It's extremely comfortable and shares all the superior qualities of the finest wool materials. It's perfect for making cosy winter clothes. The material, however, has a quite rough feel about it.
Melton Wool
Wool Melton is a heavyweight to heavy felted fabric with a bulky but smooth nap. One of its most widespread use is in coats.
Types of Wool Defined by Manufacturing Method, Quality, Etc.
Lambswool
Wool fabric made from fleece sheared from a lamb between the ages of six and seven months is meant. So, the fabric woven from this wool is very long-lasting and comfy, and it needs very little finishing. This wool is considered to be superior than all others.
Lightweight Wool
You would be mistaken if you assumed that every wool fabric was bulky and hefty. People looking for a woollen cloth with a gentle drape have many options to choose from. This fine, lightweight wool has a lovely drape because of the way it is woven—loosely but firmly. Woolen Batiste is an exquisitely soft, lightweight woollen fabric. When compared to crepe, which refers to lightweight worsted wool, albatross is a lighter woollen fabric with a somewhat crepe surface. There is also a lightweight wool challis available. Wool challis, a woollen fabric with a simple weave, is a closet staple.
Suits In Plain Or Twisted Wool
The fibres of a Worsted sheep are strong and smooth to the touch. The majority of outerwear, outerwear accessories, and outerwear accessories in stores are produced from this fabric. Worsted wool is produced by spinning wool rovings into yarn, which is then used to create high-end knitwear and woven fabrics. After the fabric is made, it goes through a procedure that gets rid of all the extra fibres, giving it a luxurious sheen.
Virgin Wool
Newly sheared lamb wool, sometimes known as "virgin wool," is exceptionally soft and smooth.
Boiled Wool
Boiled wool's insulating qualities stem from the fabric's unique stretchiness and felted weight. The special washing process used to reinforce the wool results in a finished product that is dense, long-lasting, and water-resistant. Wearables such as berets, jackets, sweaters, vests, coats, and so forth can all benefit from its incorporation.
Super Wool
Fibers from this specific breed of sheep are known for being extraordinarily fine and plush. Fibre count is a measurement of the density of a fabric and is similar to thread count. Wool is graded and priced from Extra 100 to Extra 120 to Extra 150, etc. As the number increases, the fineness of the wool increases.
Wool Chinchilla
Curled tufts or nubs cover the surface of this cloth. This one-of-a-kind sheen is the result of a fully automated chinchilla machine. The nap is manufactured by the machine, and the tufts are hand-curled from the nap.
Organic Wool
Conventional wool production frequently makes use of harmful elements like formaldehyde, conditioners, moth-proofing, extremely corrosive colours, and other, frequently hazardous additions to complete the fabric and apparel. Wool fabrics and garments produced using organic farming practises do not contain any of these toxins.
Organic wool is produced from sheep that were raised without the use of any synthetic or harmful materials. Because they are allowed to graze on pesticide-free land, sheep raised utilising organic animal husbandry practises do not contract external or internal parasites that would otherwise necessitate the use of antibiotics. Since no chemicals are used in the processing of organic wool, the resulting fabric is absolutely free of anything that could cause cancer or an allergic reaction in those susceptible to such things.
Classifying Wool According to Its Finished Fabric
Gabardine
Gabardine is a strong, tightly woven fabric that can look either diagonally corrugated (twill weave) or smooth, depending on which side you examine. Because of its durability and versatility, it is commonly used to make pants, suits, jackets, coats, and more. In addition, it can be made into practical bags.
Loden
When wet, this wool doesn't bleed like other wools. This fabric is suitable for use in creating coats.
Wool Jersey
The wool yarn used in the knitting of this cloth could have been done so by hand or by machine. It's used to make sweaters, cardigans, and other knit garments.
Boucle
It's a description of woollen fabrics with a wavy, looped texture. Because of its one-of-a-kind construction, this is the case. The looping, twisted appearance of this fabric makes it truly unique.
Wool Batting
Batting is the insulating layer inside of a duvet or comforter; batting made from wool fibres is preferable over batting made from cotton or polyester.
Broadcloth
Broadcloth made of wool is a thick and durable material.
Herringbone Patterned Wool
This wool fabric's zigzag weave was apparently influenced by the ribcage of a herring fish. Making coats and pants from this cloth should be lucrative.
Tweed
Outerwear like jackets, caps, and waistcoats, as well as cold weather accessories like gloves and scarves, are where wool tweed really shines. Its name comes from the fact that the fabric was initially made near the Tweed River in Ireland. It can be woven in a plain or twill pattern and has a mildly rough texture with an attractive check or herringbone pattern. This timeless piece is crafted from hand-spun, scratchy wool. Because it's made by twisting two and three strands of wool of different colours together, the completed product has a muted palette. This durable material will keep you warm and dry after years of use.
Wool Felt
Felted wool is an example of a non woven fabric. Wool felt predominates when discussing felt fabrics because of its durability, versatility, and affordability. This material is softer and more flexible than acrylic felt, yet it lasts far longer. It works wonderfully for making, decorating, and assembling hats, jackets, and other garments.
Lincoln Wool
Lincoln wool fabrics are highly sought after for usage in suits and other garments due to their high quality and long lifespan. It's very desirable due to its great monetary value and excellent aesthetic appeal.
Flannel
Flannel is a type of wool fabric characterised by its bristly or napped surface, which may be present on either side. It is mostly used for making pyjamas and other nightwear.
Tartan
Authentic Scottish woollen fabric typically features a timeless plain or checked pattern. The most well-known item of clothing with tartan is the Scottish kilt. It's used to create dresses, skirts, and jackets.
Chenille
The use of woollen fibres in its production gives it a plush tufted pile surface and a velvety feel.
Wool Sharkskin
Fabric made of wool with a twill weave and a smooth, two-toned appearance. Achieving the two-tone effect is as simple as alternating the white and other coloured warp and weft threads.
Classification of Wool Produced by Other Animals
Alpaca Wool
This extremely soft wool fabric is made by using the fleece of an Alpaca (a camelid). The fleece is then reversed to a cotton knit or woven basis. The fact that it doesn't aggravate allergy sufferers is this wool's biggest perk. Aside from that, it's equally as soft and warm as merino or cashmere wools of comparable quality.
Mohair
The Angora goat is responsible for producing the durable woollen fabric known as mohair, which is characterised by its luxurious softness, silky smoothness, and reflective sheen. The fabric's surface is really fuzzy. Although expensive, it is much sought after due to its perceived beauty and lavishness. It is most frequently seen in the form of coats and jackets.
Vicuna Wool
For its rarity, vicuna wool has gained a reputation as the most expensive variety of woollen textile. The price of a Vicuna jacket ranges from $6,000 to over $21,000.
Camel Hair
Weaved fabric made from the underfur of the Bactrian camel. Scarves, sweaters, jackets, and blankets are all made from tan and brown fabrics because of their plush feel. The term "camels' hair" is often used to describe thick, fluffy woollen fabrics that do not really contain any camel hair.
Impact Of Wool Fabric On The Environment
Due to the fact that wool is a by-product of the natural world, it does not harm ecosystems. If the animals utilised in the wool industry are not confined or subjected to inhumane procedures, and instead allowed to live free, happy lives, then the wool industry can be run in a sustainable manner. There is hope for a sustainable future in the wool industry, although that hasn't been proven yet. Most wool is produced in a manner that is either detrimental to the environment or cruel to the animals used in the process. An activity that humans have engaged in for millennia because of its inherent sustainability has become harmful to the environment and the animals from which wool is obtained as wool producers around the world pursue ever-greater profits at the expense of both.
Specifics on Wool
The fact that woollen garments dating back roughly 3,400 years were uncovered at an Egyptian archaeological site demonstrates that wool was regarded as helpful by ancient humans. Because not all wool fibres are the typical thickness of 28 microns, some persons experience an itching feeling when wearing wool.
Any item of clothing made from pure wool will have a S followed by a number on the label. Their precision is so high that it is utilised to specify the exact size of wires in the finished product down to the micron. You'll see the initials "Super S" followed by a number of these series on a lot of different labels. This emblem guarantees that only "virgin wool," the purest, cleanest wool available, was utilised. Labels can also indicate that rare wools like cashmere, alpaca, or mohair were combined with virgin fleece to create the Super S. The maximum value on the global scale has been set at 210.
Australian Hilton Barrett sheared a sheep in a record-breaking 39.31 seconds. Wool may be stretched to lengths up to 70% of its original size without breaking. A product can legally claim to be created from 100% natural wool in the European Union as long as it contains no and more than 5% synthetic fibres. Sheep aren't the only creatures whose hair and fur are turned into wool. The fibres may be spun into yarn, which can subsequently be used to create textiles.
Conclusion
Wool is a type of fabric made from animal hair, typically from goats or sheep. Due to the use of shorter fibres, woollen fabrics have a characteristic tufted fuzzy appearance. Carpet wool, as its name implies, is ideal for making carpets and rugs. A wide variety of contaminants can be absorbed and neutralised by wool fibres. Wool is fireproof, whereas synthetic fabrics melt at a candle's touch.
One of the many advantages of wool is its resistance to static electricity and fire. It's no secret that Merino wool is in high demand. Cashmere is a special type of wool that is both extremely expensive and incredibly comfortable to the touch. Wool Melton is a hefty or heavy felted fabric with a thick, velvety nap. Woolen batiste is a light woollen fabric with a shaggy surface texture and a luxuriously soft hand.
Spinning wool rovings into yarn creates worsted wool, which is used to make luxurious knits and textiles. It is the boiled wool's characteristic stretchiness and felted weight that gives it its insulating properties. Sheep that are bred without synthetic or hazardous elements create organic wool. Its durability and adaptability make it ideal for a wide variety of garments, including trousers, suits, jackets, coats, and more. Although it doesn't have the durability of acrylic felt, wool felt is more comfortable to work with and more pliable.
Wool Sharkskin has a twill weave and a smooth, two-tone appearance because it is composed of wool. Most expensive of all woollen fabrics is Vicuna Wool. One can spend anywhere from $6,000 to over $21,000 on a high-quality Vicuna jacket. Wool, which can be produced from synthetic fibres, can be stretched to lengths of up to 70% of its original size without breaking.
Content Summary
- Fabrics containing the fibre obtained from the fleece of a domesticated mammal are all referred to collectively as "wool."
- The average length of the fibres in the yarn used to make the fabric is one way to distinguish between woollen and Worsted fabrics.
- Blankets and sweaters can be knitted or woven with wool in a plain weave.
- This fabric has long, coarse fibres. The term "apparel wool" is used to describe the high-quality wool used for textile production.
- Woolen fabrics can be further categorised based on a variety of factors, such as the type of animal used to make them, the weave employed, the geographic origin of the wool, the fabric's texture, etc.
- Wool: An Explanation
- Wool is a type of fabric made from animal hair, typically from goats or sheep.
- Wool's advantages include its resilience and long lifespan. in opposition to wetness The interaction between wool's two types of fibre is what gives it its moisture-regulating properties.
- Integrated Self-Sanitation System Wool can clean itself mechanically thanks to the unique structure of its fibres.
- The two kinds of fibres that make up the filament trunk's interlaced liana structure swell and shrink to varying degrees when water is taken in and expelled.
- They clustered so closely that they set the wool fibre moving.
- The filth does not get embedded in the fibres, but rather sits on top.
- Wool is naturally resistant to dirt because of this property.
- Auto-Cleaning Materials The chemical self-cleaning abilities of wool contribute to its amazing softness.
- Wool fibres have the unique ability to absorb and neutralise a wide variety of pollutants due to their physical and chemical composition.
- That's why, even when they're soiled, wool garments don't give off an offensive odour.
- Fire-Retardant and Anti-Static The fact that wool is resistant to both static electricity and fire is a bonus.
- Wool is fireproof, whereas synthetic fabrics melt at a candle's touch.
- The lack of static charge that wool possesses is an advantage for many people, especially those who have experienced a "spark" while touching a metal door handle or whose hair has stood on end after wearing synthetic clothing.
- Diversity in Wool Sheep's Wool From Merino Sheep It's no secret that Merino wool is in high demand.
- Australia is home to the vast majority of the world's merino sheep, and the country's wool is widely used in manufacturing.
- Cashmere is a type of wool known for its extreme softness and high price.
- Cashmere goats, whose wool is used to make cashmere products, are native to the region of Kashmir in northern India.
- It's Made with Border Leicester Wool Beautiful The Border Leicester long wool breed of sheep has a long history in the Border Leicester region of England, hence the name of the fabric made from this wool.
- Textile coatings are widely used.
- Fine, Featherweight Wool If you think that all wool fabrics are heavy and cumbersome, you'd be wrong.
- There are numerous possibilities for those seeking a woollen fabric with a soft drape.
- High-quality and soft-to-the-touch, that's how Worsted sheep's fibres are described.
- The vast majority of jackets, coats, and similar items sold in stores are made from this material.
- Raw Wool Virgin wool, the name given to wool that has just been sheared from a lamb, is incredibly soft and smooth.
- Tanned Wool The elasticity and felted weight of boiled wool contribute to the fabric's insulating properties.
- Ultra Fine Wool The fleeces of these sheep are prized for their luxurious softness and extraordinary fineness of fibre.
- Wool from the Chinchilla This fabric is covered in little tufts or nubs that have been curled up.
- A fully automated chinchilla machine produced this one-of-a-kind shine.
- Products made from wool that were grown using organic methods do not contain any of these chemicals.
- Sheep used in the production of organic wool were not given any synthetic or potentially harmful substances during their upbringing.
- Its durability and adaptability make it ideal for a wide variety of garments, including trousers, suits, jackets, coats, and more.
- It's possible to make coats out of this material.
- A Wool Jersey This fabric, knit from wool yarn, could have been made either by hand or by machine.
- It's mostly employed in the production of knitwear like sweaters and cardigans.
- Boucle Woolen fabrics with a wavy, looped texture are being described here.
- Wool broadcloth is a thick and long-lasting fabric.
- Herringbone Embroidered Wool Fabric The skeleton of a herring fish may have been an inspiration for the zigzag weave of this wool fabric.
- Coats and pants crafted from this fabric have the potential to be profitable.
- The first production of this fabric took place near the Tweed River in Ireland, hence the name.
- You can weave it into a pretty check or herringbone pattern, and it has a somewhat gritty texture that looks great either plain or twilled.
- Fabricated From Merino Wool Felt Non woven materials include, for instance, felted wool.
- Wool felt is the most commonly mentioned felt fabric because it is long-lasting, adaptable, and inexpensive.
- A Scottish kilt is the most well-known piece of clothing to feature tartan.
- Vicuna Fiber Vicuna wool is the most expensive type of wool because of its scarcity.
- Wool's Negative Effects on Nature as a Fabric Wool is a natural by-product, thus it has no negative impact on the environment.
- Animals used for wool production can contribute to sustainability in the industry if they are not confined or subjected to inhumane procedures, but rather allowed to live free, happy lives.
- As wool producers around the world pursue ever-greater profits at the expense of the environment and the animals from which wool is obtained, a practise that has been practised by humans for millennia because of its inherent sustainability has become harmful to both.
- Descriptions of Wool The fact that 3,400-year-old woollen clothing was discovered at an Egyptian archaeological site suggests that ancient people found wool to be useful.
- Some people get an itchy feeling when wearing wool because not all wool fibres are the standard thickness of 28 microns.
- The label on 100% wool clothing will have a S followed by a number.
- Because of their extreme accuracy, they are used to define the micron-level dimensions of wires in the final product.
- Many of these series are denoted by the letters "Super S" followed by the series name.
- The use of this symbol ensures that only "virgin wool," the cleanest and most pristine wool on the market, was employed.
- If the Super S was made with a combination of virgin fleece and a more expensive wool, such as cashmere, alpaca, or mohair, the label will indicate that. For the entire world, 210 is the cap that has been established.
- In a world record time of 39.31 seconds, Australian Hilton Barrett sheared a sheep.
- The length to which wool can be stretched without breaking is approximately 70% of its initial length.
- In the European Union, a product can legitimately claim to be made from 100% natural wool if it contains no synthetic fibres and no more than 5% natural fibres.
- It's not just sheep whose hair and fur are processed into wool.
- To make cloth, the fibres can be spun into yarn.