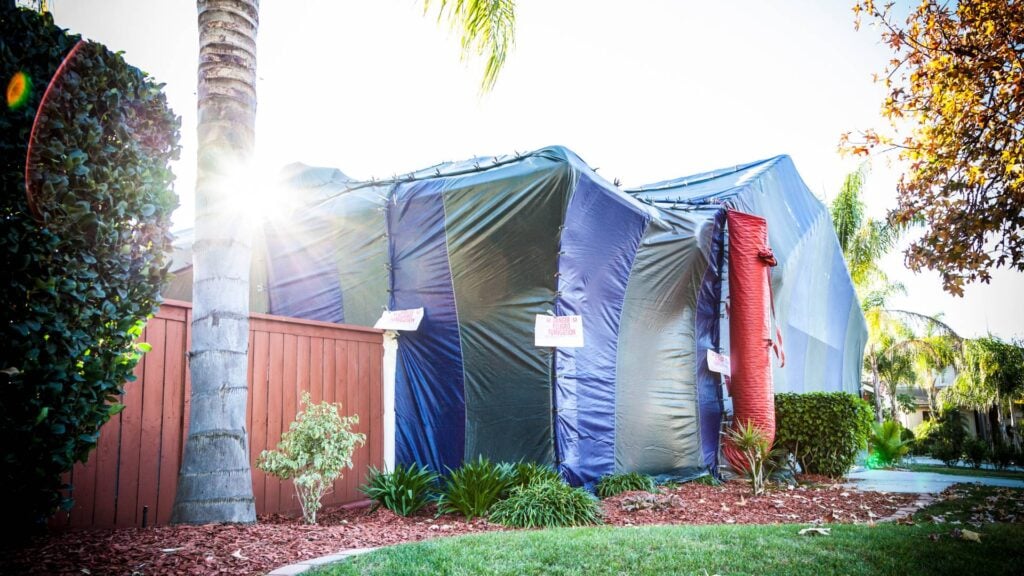
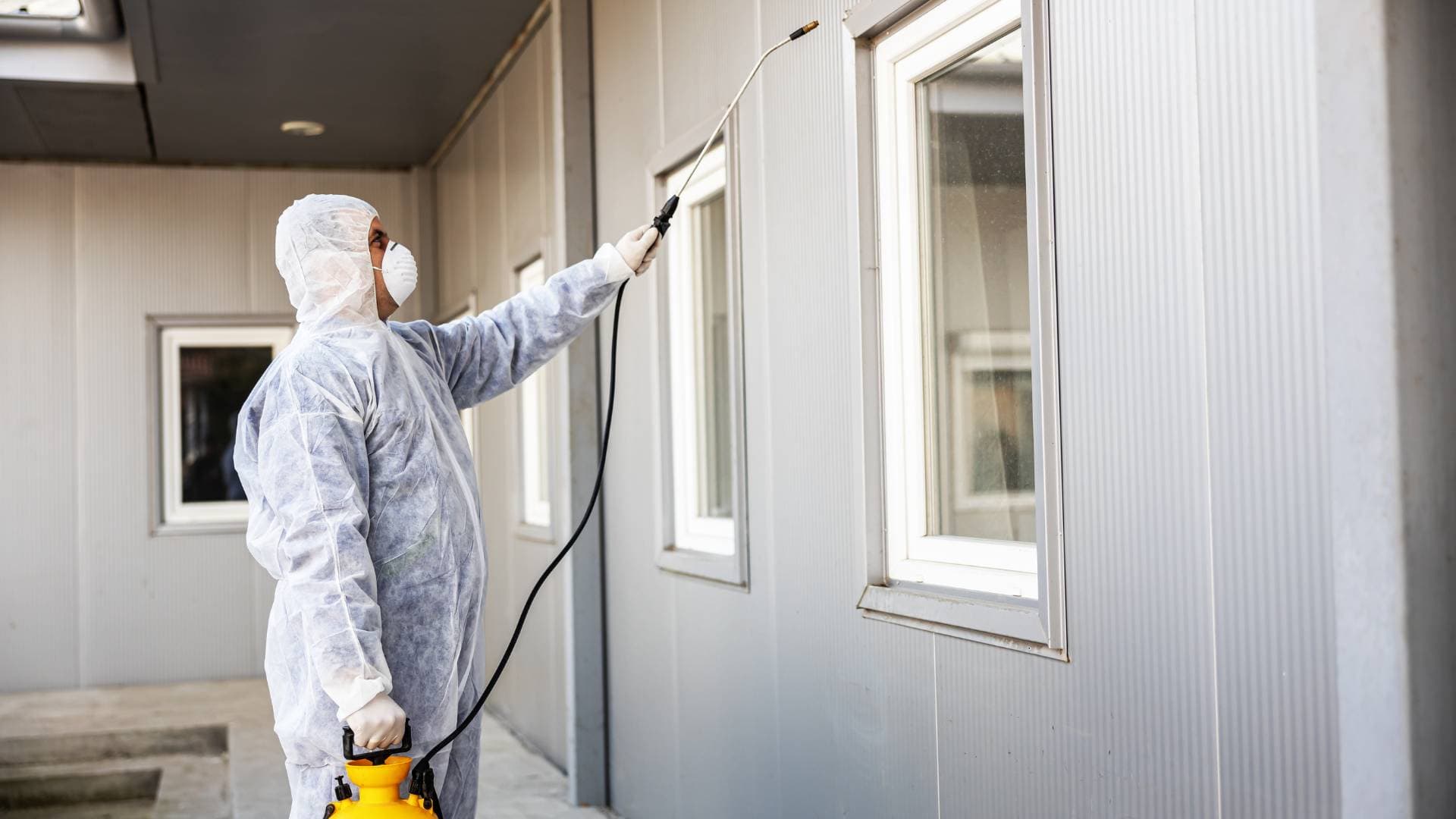
Termite fumigation is a widely used method for tackling severe infestations, offering a potent solution to eliminate these destructive pests from our homes and buildings. While the effectiveness of this approach is well-documented, it's crucial to consider the broader implications, particularly the potential side effects on human health and the environment. Using chemical fumigants raises important questions about safety, making it essential for homeowners and residents to know what to expect during and after the fumigation process.
In this blog, we delve into the side effects of termite fumigation, exploring how it impacts not just the termites but also the people and the world around us. From health concerns to environmental considerations, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview to help you make informed decisions about managing termite infestations. Join us as we uncover the unseen consequences of termite fumigation, shedding light on the precautions and alternatives available to safeguard our health and protect our planet.
What Are the Health Risks of Termite Fumigation for Humans and Animals?
While termite fumigation is a highly effective method for eradicating termite infestations, it raises significant health concerns for humans and animals. The process involves using potent chemical fumigants that can pose significant health risks if exposure occurs before, during, or after the tenting process. Understanding these risks is crucial for ensuring the safety of all occupants and pets during and after fumigation.
Key Health Risks And Safety Measures
- Chemical Exposure: The primary concern with termite fumigation is the exposure to chemical fumigants, which can lead to serious health issues, including respiratory problems, skin irritation, and, in severe cases, even death. These chemicals are designed to penetrate deep into the structure to eliminate termites but can also linger, posing risks to humans and pets.
- Respiratory Issues and Allergic Reactions: Individuals with pre-existing conditions such as asthma or allergies may be more susceptible to the effects of fumigation chemicals. Termite frass (droppings and debris) can become airborne during and after fumigation, potentially leading to respiratory issues and allergic reactions.
- Preventive Measures: Professional pest control companies take extensive precautions to prevent human and pet exposure to fumigants. This includes thoroughly inspecting and preparing the property, ensuring that all occupants and pets have vacated the premises, and sealing the structure with tarps to contain the chemicals.
- Post-Fumigation Safety: After fumigation, allowing the chemicals to dissipate fully before re-entering the home is essential. Certified technicians measure chemical levels for at least 24 hours post-fumigation to ensure safety. The home is then aired for 24 hours to reduce chemical concentrations further.
- Long-Term Health Effects: While immediate exposure to fumigation chemicals poses acute risks, there is concern about the potential long-term health effects of low-level exposure to these chemicals. Ongoing research aims to understand these risks better and develop safer fumigation practices.
Recommendations For Homeowners
- Follow Professional Advice: Adhere strictly to the guidelines provided by your pest control service regarding preparation for fumigation and re-entry into your home.
- Ventilation: Ensure your home is adequately ventilated after fumigation to remove residual chemicals.
- Cleaning: Consider deep cleaning your home post-fumigation to eliminate any remaining traces of fumigants.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you experience health issues after re-entering your home, seek medical attention immediately.
How Does Termite Fumigation Affect the Environment?
Termite fumigation, mainly using sulfuryl fluoride, poses significant environmental concerns beyond its intended pest control applications. This chemical, the only fumigant approved by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for residential use, is a potent greenhouse gas with far-reaching implications for global warming and ecosystem health.
The Greenhouse Gas Dilemma
Sulfuryl fluoride is identified as a potent greenhouse gas with a long atmospheric lifetime of approximately 36 years. Its global warming potential is alarmingly high, with 1 ton of sulfuryl fluoride trapping as much heat in the atmosphere as 7,510 tons of carbon dioxide over a 20-year interval. Despite its effectiveness against termites, the environmental cost of its use is significant, contributing to climate change at a scale that demands urgent attention.
The California Case
With its warm climate conducive to termite infestations, California significantly contributes to sulfuryl fluoride emissions. The state's extensive use of this chemical for termite fumigation highlights a critical environmental challenge. At the same time, California provides a statewide record of sulfuryl fluoride use and its emissions' broader implications concern global environmental health.
Human And Wildlife Risks
Aside from its environmental impact, sulfuryl fluoride poses direct risks to human health and wildlife. As a biocide, it indiscriminately kills living organisms exposed to high concentrations over time, including humans, pets, plants, and wildlife. The EPA has set exposure limits to protect against these risks. Still, accidental deaths and the potential for long-term health effects underscore the need for stricter regulations and safer alternatives.
The Path Forward
Including sulfuryl fluoride in future greenhouse gas inventories and emissions reduction, targets is crucial to mitigating its environmental impact. Research led by Dylan Gaeta at Johns Hopkins University underscores the urgency of addressing sulfuryl fluoride emissions, advocating for national, state, and local measures to curb its contribution to climate change.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Followed Before, During, and After Termite Fumigation?
Termite fumigation involves significant preparation and adherence to safety measures to protect your property and ensure the health and safety of your family and pets. Here's a comprehensive guide to the safety precautions and best practices recommended before, during, and after termite treatment, combining insights from various expert sources.
Before Fumigation: Preparation Is Key
- Understand Treatment Options: Familiarise yourself with the different termite treatment methods, including chemical barriers, baiting systems, and natural alternatives. Each comes with specific safety considerations.
- Choose Safe Chemical Treatments: If opting for chemical treatments, understand the types of chemicals used, their potential risks, and the safety measures professionals recommend. Hiring licenced pest control experts is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
- Opt for Non-Chemical Solutions: For those preferring safer alternatives, explore baiting systems and natural methods. These options emphasise safety and minimise the impact on family members and pets.
- DIY Termite Control Safety: If you're considering a DIY approach, follow comprehensive safety guidelines, including wearing protective gear and applying treatments correctly.
- Home Preparation: Secure food items, remove pets from the treatment area, and ensure adequate ventilation to mitigate risks associated with termite treatments.
During Fumigation: Vigilance And Safety
- Follow Technician's Instructions: To avoid safety issues during treatment, adhere strictly to the guidelines provided by your pest control service.
- Temporary Relocation: Depending on the treatment method, consider temporarily relocating kids, elderly family members, and pets to ensure their safety.
- Secure and Remove Food Items: To prevent contamination, protect and remove food items from your home, especially if termite sprays are used.
After Fumigation: Ensuring a Safe Return
- Post-Treatment Cleaning: Thoroughly clean your home after treatment to remove any residues and ensure a safe environment for your family.
- Termite Prevention: Take proactive steps to prevent future infestations, such as removing dead wood from your property and repairing water leaks promptly.
- Consult Professionals: Always consult with pest control professionals for a thorough inspection, suitable treatment recommendations, and tailored safety measures for your home.
Legal And Regulatory Considerations
Legal and regulatory considerations are paramount when planning and executing termite fumigation treatments. These considerations ensure that the process is effective and compliant with local and national standards, safeguarding both the environment and public health. Here's a synthesis of insights from various sources on the legal and regulatory aspects of termite fumigation:
- Understanding Fumigant Dynamics: The effectiveness of fumigation is significantly influenced by the physical and biological characteristics of the target pests and environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of oxygen or carbon dioxide. Recognising these factors is crucial for selecting the appropriate fumigant and applying it to ensure maximum penetration and pest eradication.
- Optimising Environmental Conditions: Temperature and humidity play critical roles in the efficacy of fumigants. Higher temperatures enhance the fumigant's volatility and the pests' metabolic rate, making them more susceptible. Maintaining optimal moisture levels can facilitate the generation of fumigant gas from solid or liquid formulations and improve penetration into pest-infested materials.
- Sealing and Structural Integrity: Achieving a gas-tight environment is essential for the success of fumigation. Proper sealing of the fumigation space prevents the escape of fumigants, ensuring that they remain in contact with the pests for the required duration to achieve complete eradication.
- Controlled Atmosphere Techniques: Modifying the atmosphere within the storage or fumigation space by reducing oxygen levels or increasing carbon dioxide concentrations can serve as an effective alternative or complement to traditional chemical fumigation.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Incorporating fumigation into a broader IPM strategy can enhance its effectiveness and sustainability. This involves combining fumigation with other pest control methods, such as biological controls, physical barriers, and sanitation practices, to manage pest populations, reduce reliance on chemical treatments, and mitigate the risk of pest resistance.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: Regular monitoring of pest populations and their response to fumigation treatments is essential for adapting strategies to changing conditions and emerging challenges, such as developing resistance to certain fumigants.
Conclusion
Termite fumigation is a widely used method for eliminating termite infestations in homes and buildings. However, it raises significant health and environmental concerns. The use of chemical fumigants can pose serious health risks, including respiratory problems, skin irritation, and even death. People with pre-existing conditions like asthma or allergies may be more susceptible to the effects of fumigation chemicals.
Professional pest control companies take extensive precautions to prevent human and pet exposure to fumigants, including thorough inspections, vacating premises, and sealing the structure with tarps. Post-fumigation safety is essential, with certified technicians measuring chemical levels for at least 24 hours post-fumigation and allowing the home to air out for an additional 24 hours. Long-term health effects of low-level exposure to these chemicals are also a concern.
Termite fumigation, mainly using sulfuryl fluoride, poses significant environmental concerns beyond its pest control applications. This chemical, the only fumigant approved by the EPA for residential use, is a potent greenhouse gas with far-reaching implications for global warming and ecosystem health. The California case highlights the broader implications of its emissions, with the state's extensive use of sulfuryl fluoride contributing to global environmental health.
The EPA has set exposure limits to protect against these risks. Still, accidental deaths and the potential for long-term health effects underscore the need for stricter regulations and safer alternatives. Including sulfuryl fluoride in future greenhouse gas inventories and emissions reduction targets is crucial to mitigating its environmental impact.
Termite fumigation is a crucial process that requires careful preparation and adherence to safety measures. Before treatment, it is essential to understand the various termite treatment methods, choose safe chemical treatments, and follow safety guidelines. For DIY termite control, follow safety guidelines, secure food items, and ensure adequate ventilation. Following the technician's instructions during treatment, temporarily relocate children, elderly family members, and pets, and secure and remove food items. Post-treatment, ensure a safe return by cleaning thoroughly and taking proactive steps to prevent future infestations. Consult pest control professionals for a thorough inspection and tailored safety measures.
Legal and regulatory considerations are crucial when planning and executing termite fumigation treatments. Understanding the effectiveness of fumigation is crucial, as the physical and biological characteristics of the pests and environmental conditions influence it. Optimising environmental conditions, sealing and structural integrity, controlled atmosphere techniques, integrated pest management (IPM), and continuous monitoring are essential for effective and sustainable termite control. By incorporating fumigation into a broader IPM strategy, pest populations can be managed more effectively and mitigated, ultimately ensuring the safety and health of your property.
Content Summary
- Termite fumigation is a potent method to eliminate severe infestations in homes and buildings.
- It's essential to consider the broader implications of fumigation, especially its potential side effects on human health and the environment.
- The use of chemical fumigants in termite fumigation raises safety questions.
- Homeowners and residents must know what to expect during and after the fumigation process.
- The blog explores the side effects of termite fumigation on people and the environment.
- Health and environmental considerations are discussed to help inform decisions about termite infestation management.
- Termite fumigation involves using potent chemical fumigants that pose significant health risks.
- Exposure to chemical fumigants can lead to serious health issues, including respiratory problems, skin irritation, and even death.
- Professional pest control companies take extensive precautions to prevent exposure to fumigants.
- After fumigation, it's essential to allow the chemicals to dissipate fully before re-entering the home.
- Concern exists about the potential long-term health effects of low-level exposure to fumigation chemicals.
- Homeowners should follow professional advice, ensure adequate ventilation, and consider deep cleaning their homes post-fumigation.
- Sulfuryl fluoride, used in termite fumigation, is a potent greenhouse gas with significant environmental concerns.
- Its global warming potential is alarmingly high, contributing to climate change.
- California significantly contributes to sulfuryl fluoride emissions due to its warm climate, which is conducive to termite infestations.
- Sulfuryl fluoride poses direct risks to human health and wildlife.
- The EPA has set exposure limits to protect against these risks.
- Research underscores the urgency of addressing sulfuryl fluoride emissions to mitigate its environmental impact.
- Termite fumigation requires significant preparation and adherence to safety measures.
- Understanding different termite treatment methods and their safety considerations is crucial.
- Opting for non-chemical solutions and DIY termite control safety are discussed.
- Following the technician's instructions and securing food items during fumigation are essential safety measures.
- Post-fumigation, engaging in thorough cleaning and termite prevention is recommended.
- Legal and regulatory considerations ensure the fumigation process is compliant with standards.
- Understanding fumigant dynamics and optimising environmental conditions are essential to effective fumigation.
- Achieving a gas-tight environment and integrating fumigation into a broader pest management strategy are essential.
- Regular monitoring and adaptation of strategies are necessary to address emerging challenges.
- The blog aims to provide a comprehensive overview of termite fumigation's side effects.
- It sheds light on precautions and alternatives to safeguard health and protect the planet.
- The effectiveness of termite fumigation and its impact on termites and humans are explored.
- The blog discusses the unseen consequences of termite fumigation.
- Safety precautions and protective measures are crucial for ensuring well-being post-fumigation.
- The importance of ventilation and cleaning after fumigation is emphasised.
- Health monitoring for symptoms of chemical exposure is advised.
- Recommendations for homeowners include following professional advice and seeking medical attention if needed.
- The environmental impact of termite fumigation, especially using sulfuryl fluoride, is significant.
- The greenhouse gas dilemma and the California case highlight the environmental challenges.
- Human and wildlife risks from sulfuryl fluoride exposure are discussed.
- The path forward includes addressing sulfuryl fluoride emissions and exploring safer alternatives.
- Safety measures and best practices for termite fumigation are outlined.
- Preparation before fumigation and vigilance during the process are emphasised.
- Ensuring a safe return after fumigation involves cleaning and termite prevention.
- Legal and regulatory considerations focus on compliance with standards and environmental protection.
- The blog provides insights into the complexities of termite control and the importance of informed decision-making.
- Understanding the risks and benefits of termite fumigation helps homeowners protect their properties.
- The blog encourages exploring non-chemical and safer termite treatment alternatives.
- It highlights the need for professional advice and strict adherence to safety guidelines.
- The environmental and health concerns associated with termite fumigation underscore the importance of responsible pest management.
- The blog serves as a resource for homeowners seeking to navigate the post-fumigation landscape safely.
- It aims to raise awareness about the side effects of termite fumigation and promote safer, more sustainable pest control practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Immediate health risks can include respiratory irritation, skin irritation, nausea, and headaches due to exposure to chemical fumigants used during the process.
Yes, there is concern about potential long-term health effects, including neurological damage and an increased risk of cancer, from exposure to fumigation chemicals.
Yes, pets and wildlife are also at risk from exposure to the toxic chemicals used in fumigation. It's crucial to ensure they are safely relocated during the process.
Termite fumigation can have significant environmental impacts, including contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and affecting non-target organisms due to potent chemical fumigants like sulfuryl fluoride.
Ensure thorough ventilation of the treated area post-fumigation, follow all safety guidelines provided by the pest control professionals, and consider deep cleaning your home to remove any residual chemicals.